In the world of real estate and home financing, the Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio plays a pivotal role in determining your eligibility for a mortgage.
This crucial financial metric offers lenders insights into your ability to manage monthly mortgage payments while balancing your existing debts.
Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or looking to refinance, understanding your DTI ratio is essential for making informed decisions.
In this article, we will explore what a Debt-to-Income ratio is, how it’s calculated, why it matters, and tips to improve it, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your real estate journey.

What is a Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Your Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio is a financial measure that compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. It is expressed as a percentage and is used by lenders to assess your ability to to repay a loan. This includes your mortgage payment, credit cards, other loans, and more. It’s calculated like this:
(Total monthly debt) / (Gross monthly income) x 100 = DTI
Essentially, your DTI ratio helps lenders determine how much of your income is already committed to debt obligations. This in turn influences how much additional debt you can comfortably take on, such as a mortgage.
Types of DTI Ratios
There are two primary types of DTI ratios that lenders consider: the front-end ratio and the back-end ratio. Read on to learn more about the two types of DTI ratios.
Front-End Ratio:
The front-end ratio, also known as the housing ratio, represents the percentage of your income that goes toward housing expenses. It includes mortgage payments, property taxes, homeowners insurance, and, if applicable, HOA fees. This ratio helps lenders determine if you can afford the home you want to buy based on your income.
For example, if your gross monthly income is $6,000, and your housing expenses total $1,500, your front-end DTI ratio would be 25%. Lenders typically prefer a front-end ratio of 28% or lower.
Back-End Ratio:
The back-end ratio is more comprehensive, as it includes all your monthly debt obligations. This ratio considers not only housing expenses but also other recurring debts. This includes your housing expenses, plus car loans, student loans, credit card payments, personal loans, etc.
The back-end ratio provides a broader view of your financial situation and helps lenders assess your overall debt burden. Living expenses, such as utilities, are not included, however.
For example, if your total monthly debts amount to $2,400 and your gross monthly income is $6,000, your back-end DTI ratio would be 40%. Most lenders prefer a back-end ratio of 36% or lower. Although, some may allow up to 43% or higher under certain circumstances.
How Do I Calculate My Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Calculating your DTI ratio is relatively straightforward. Follow these steps to calculate your back-end DTI:
- Calculate Your Total Monthly Debt Payments: Add up all your monthly debt obligations, including housing expenses. This should include your mortgage or rent payment, car loan, student loans, credit card minimum payments, and any other recurring debt. If you’re applying with someone else, combine both of your monthly debts. Don’t include other monthly expenses like food and utilities.
- Divide Your Debts by Your Monthly Gross Income: Next, divide your debt payments by your pre-tax monthly income. Again, make sure you’re using the combined debts and income of all mortgage applicants.
- Multiply the Result by 100 to Express DTI as a Percentage: The final step is to convert your DTI ratio from a decimal to a percentage by multiplying it by 100. The lower your DTI, the better your odds of approval for new credit.
For example, if your total monthly debt payments are $2,000 and your gross monthly income is $6,000, your DTI ratio would be:
($2,000) / ($6,000) x 100 = 33.33%
This means 33.33% of your gross income is dedicated to paying off debt each month.

Why Does Your Debt-to-Income Ratio Matter?
Your Debt-to-Income ratio matters because it serves as a key indicator of your financial health and your ability to manage additional debt responsibly. For lenders, the DTI ratio is a critical factor in determining your eligibility for a mortgage and other types of loans.
A higher DTI ratio suggests that a larger portion of your income is tied up in debt payments. This may indicate a higher risk of defaulting on new debt obligations.
Conversely, a lower DTI ratio indicates that you have a more manageable level of debt relative to your income. This makes you a more attractive candidate for lenders.
A strong DTI ratio will improve your chances of getting approved for a mortgage. It can also help you secure more favorable terms, such as lower interest rates.
What is a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio?
A “good” Debt-to-Income ratio varies depending on the lender and the type of loan you’re seeking. A good debt-to-income ratio is one that is as low as possible. A low DTI may improve your odds of approval for loans and credit cards with low interest rates.
It’s worth noting, different lenders follow different eligibility criteria, and their DTI ranges often vary. An “ideal” DTI for one lender may be a dealbreaker for another, and vice-versa.
However, general guidelines can help you understand where you stand:
- Front-End Ratio: Lenders typically prefer a front-end DTI ratio of 28% or lower. This suggests that less than 28% of your gross income goes toward housing costs, indicating that you can comfortably afford the home without stretching your budget too thin.
- Back-End Ratio: A back-end DTI ratio of 36% or lower is often considered ideal. This ratio indicates that your overall debt burden is manageable and that you have sufficient income left over to cover other expenses and savings.
Keep in mind, some lenders may approve loans for borrowers with higher DTI ratios. Other factors, such as a high credit score, a substantial down payment, or significant cash reserves can influence a lender’s decision.

What DTI Ratio Do You Need for a Mortgage?
When it comes to securing a mortgage, different loan programs have varying DTI requirements. Understanding these requirements can help you determine what type of mortgage you may qualify for. Here’s a quick look at what the general, DTI requirements look like by loan type:
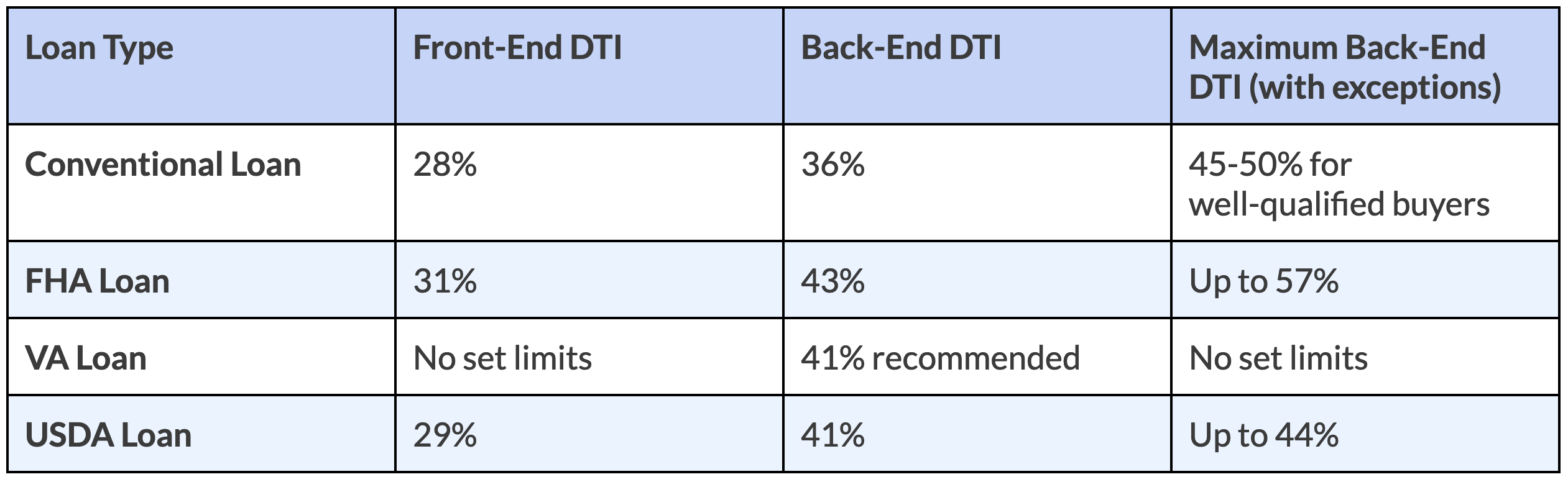
Conventional Loans:
For conventional mortgages, lenders typically prefer a maximum front-end DTI ratio of 28% and a maximum back-end DTI ratio of 36%. However, some lenders may allow back-end ratios as high as 50%, especially for borrowers with strong credit profiles. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFBP) shows the median DTI of conventional borrowers is 37%.
FHA Loans:
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) is more lenient with DTI ratios. Borrowers may qualify for an FHA loan with a front-end DTI ratio of up to 31% and a back-end DTI ratio of up to 43%.
Lenders may also make exceptions for DTI ratios up to 57% if the applicant has mitigating factors like a large down payment or a lot of liquid assets. According to the CFPB, the median DTI of FHA borrowers is 44%.
VA Loans:
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) technically sets a maximum back-end DTI of 41%. However, a back-end DTI ratio of 41% or lower is generally preferred on VA loans.
VA lenders may allow higher ratios if the borrower has strong residual income (income left over after paying monthly debts). In fact, according to the CFPB, the median DTI for VA borrowers is 42%.
USDA Loans:
For USDA loans, which are backed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the standard maximum DTI ratio is 29% for the front-end and 41% for the back-end. As with other loan types, exceptions can be made for borrowers with strong compensating factors. The CFPB shows that 36% is the median DTI for USDA borrowers.

Tips for Improving Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Improving your Debt-to-Income ratio can enhance your financial profile and increase your chances of qualifying for a mortgage with favorable terms. It can also qualify you for better terms and interest rates.
So even if your DTI is under the maximum threshold, you might consider working on your ratio before applying for your loan. Here are some strategies to help you lower your DTI ratio:
- Pay Down Existing Debt: Focus on reducing high-interest debt, such as credit card balances, personal loans, and car loans. Making extra payments towards these debts can lower your monthly obligations and improve your DTI ratio.
- Avoid Taking on New Debt: While you’re preparing to apply for a mortgage, avoid taking on additional debt, such as new credit cards or loans. New debt increases your monthly payments and can negatively impact your DTI ratio.
- Increase Your Income: Consider ways to boost your income, such as taking on a side job, freelancing, or asking for a raise at work. Increasing your gross income can help lower your DTI ratio by widening the gap between your income and debt obligations.
- Refinance Existing Loans: If possible, consider refinancing high-interest loans to lower interest rates and reduce your monthly payments. This can help lower your DTI ratio by decreasing the amount you owe each month.
- Pay Off Smaller Debts: Paying off smaller debts can have a significant impact on your DTI ratio, especially if the monthly payments were relatively high. Clearing these debts can free up income for other obligations.
- Make a Larger Down Payment: When purchasing a home, making a larger down payment can reduce the loan amount you need, which in turn lowers your monthly mortgage payment and improves your DTI ratio.

Key Takeaways: What is DTI & Why Does it Matter?
Your Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio is a crucial financial metric.
It plays a significant role in your ability to qualify for a mortgage and manage your finances effectively.
By understanding your DTI ratio, you can make informed decisions about managing your debt.
It aslo improves your chances of securing favorable mortgage terms.
A good DTI ratio is typically below 36%, though specific requirements vary depending on the loan type.
Improving your DTI ratio through debt reduction, income increases, and careful financial planning can enhance your financial health and make homeownership more attainable.
As you navigate the mortgage process, keep your DTI ratio in mind.
Take proactive steps to ensure you’re in the best possible position to achieve your real estate goals.
If you’re ready to get started on your home-buying journey, Helen Painter Group Realtors is here to offer our expertise and local knowledge.
A long-standing and trusted Fort Worth real estate agency, we’ve been serving buyers and sellers since 1958.
With over six decades of success behind us, you’ll surely have peace of mind knowing your best interests are being represented each step toward buying or selling a home.
To learn more or speak with an agent, feel free to give us a call at (817) 923-7321 or contact us.

