When it comes to borrowing money for a mortgage, not everyone has the same choices available. If you are a qualified active-duty service member, a veteran, or a surviving spouse, you could consider a VA loan.
VA loans from the Department of Veterans Affairs are known for being cost-effective and having adaptable criteria.
Choosing whether to get a VA loan or a conventional loan is an important decision when you want to become a homeowner. For those who meet the requirements, VA loans are often the best choice because they offer unique advantages.
Yet, they are not the only option. Traditional loans may also provide competitive interest rates depending on the lender and your financial situation. So, how do you decide between a VA loan vs. a conventional loan when purchasing or refinancing a home?
In this article, we will discuss why VA loans are the preferred option for eligible borrowers. We will highlight the benefits that set them apart and provide useful information to help you make an informed decision when buying a home.

What are the Differences Between VA vs. Conventional Loans?
When you’re faced with the decision of whether to go with a VA loan or a conventional mortgage, it can often feel like a tough choice. Even though some of the requirements for VA loans may overlap with conventional loans, there are key differences that set them apart from each other.
To help you understand the differences better, take a look at the table provided below. It highlights the essential factors you should consider when comparing VA loans and conventional loans.
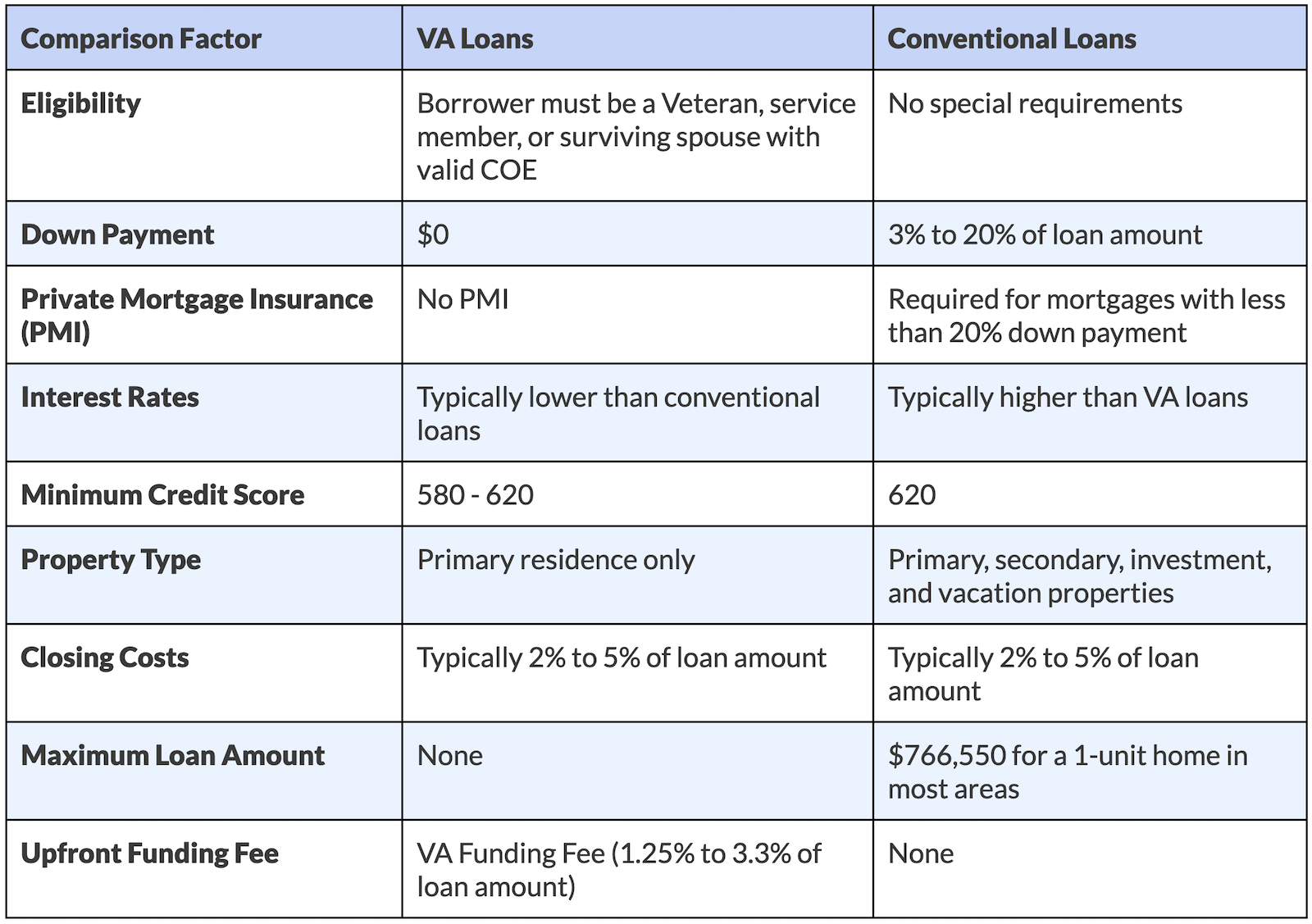
Let’s explore the specifics of several factors and understand situations when one loan type might be more favorable than the other.
Eligibility
The first criterion in our comparison of VA loans vs. conventional loans is eligibility. This may seem pretty obvious, but we want to make sure we cover our bases.
VA Loans
The most important distinction between the two types of loans lies in the eligibility criteria. VA loans are specifically designed for Veterans, active duty military personnel, and surviving spouses who possess a valid Certificate of Eligibility (COE). Individuals who fail to meet these fundamental service-related prerequisites are ineligible for a VA loan.
Conventional Loans
Conventional loans are loans that typically do not come with any specific borrower criteria or requirements that need to be met. This means that as long as an individual possesses the necessary credit standing and financial stability, they could potentially qualify for a conventional loan.
Down Payment
If you’re having trouble saving for a down payment, consider a VA loan. Yet, conventional loans often ask for lower down payments than you might think.
VA Loans
A VA loan lets you skip a down payment, with only a few borrowers choosing to put money down. However, zero down could mean more interest payments in the long run compared to those who make a down payment. It also risks leaving you with negative equity—a concern when selling.
Your lender might still ask for a down payment if your credit score is low. They might also require a down payment if the property’s price is high. This is especially common in a competitive market with many offers.
Conventional Loans
To get a conventional loan, you usually need at least a 3% down payment. Lenders that offer conventional loans typically prefer larger down payments. The minimum may be 3%, but they recommend 20% or larger. By doing so, you avoid paying mortgage insurance. Some programs might allow for a 0% down payment if you qualify as a low-income earner or first-time homebuyer.
Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)
VA loans are more generous compared to other low-down-payment mortgages because they do not need monthly mortgage insurance payments. Yet, borrowers must pay a significant fee that conventional loans do not require.
VA Loans
VA loans don’t ask low-down-payment borrowers to pay PMI, but they usually need to pay a VA funding fee. This fee can vary from 1.4% to 3.6% of the total loan amount, based on your down payment and if you’re a first-time VA borrower.
You can pay the fee in cash when closing or include it in the mortgage. If added to the mortgage, it will end up costing more over time since you’ll be paying interest on it throughout your whole loan duration. Consequently, your monthly payment will be slightly higher.
Conventional Loans
With conventional loans borrowers who put down less than 20% are required to buy private mortgage insurance. The less you put down and the lower your credit score, the more PMI you pay. Some lenders might charge a higher interest rate and waive your PMI requirement (they pay the PMI themselves instead), but that might not be a better deal. Borrowers can pay PMI upfront like a VA funding fee.
Most borrowers pay it monthly until their home equity hits 20%. Then, you can remove PMI.
Interest Rates
When comparing mortgage rates for VA loans and conventional loans, your financial strength as a borrower may have a greater impact than the specific loan type. VA loans could be somewhat more affordable, but this varies based on the mortgage lender and your financial profile.
VA Loans
VA loan rates usually are the lowest in the market. In 2023, based on data from Optimal Blue, VA loan rates were on average .323 percent lower than conventional loan rates.
While a .323 percent difference might seem minor, it could mean saving tens of thousands of dollars in interest over the mortgage’s lifespan.
VA loans, supported by the Department of Veterans Affairs, provide lenders with the assurance to offer better rates to borrowers, even those with less-than-perfect credit.
Conventional Loans
For individuals who have superb credit scores of 720 or above, the interest rates offered on conventional mortgages typically appear quite comparable to those of VA mortgages.
Credit Score
Your credit score plays an important role in your eligibility, borrowing capacity, and interest rate. Regardless of the type of mortgage you use to buy a home, improving your credit score will have a positive impact.
VA Loans
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) doesn’t specify a credit score requirement for VA loans, but most lenders do. Similar to regular loans, VA lenders typically prefer a mortgage credit score of 620 or higher. However, some VA lenders may consider credit scores as low as 580.
Even with a poor credit score, you might still qualify for a VA loan by meeting specific “compensating factors” like a good debt-to-income ratio, a stable job history, or a positive track record of owning homes in the past. Another option is to work with a credit advisor to enhance your credit score.
Conventional Loans
Requirements differ between lenders but, you typically need a credit score of at least 620 to be eligible for a conventional loan. However, some lenders might ask for a higher score than that.
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
During the mortgage underwriting process, your lender will review your debt-to-income ratio (DTI). This ratio indicates the portion of your gross income allocated to debt monthly. It helps the lender assess if you can realistically manage the monthly mortgage payments you are seeking based on your current financial situation.
Below is the equation used to calculate your DTI:
(Total monthly debt) / (Gross monthly income) x 100 = DTI
VA Loans:
The VA accepts borrowers with any DTI ratio. VA lenders, however, generally favor a DTI below 41%.
Conventional Loans:
You might qualify for a conventional mortgage with a DTI ratio up to 50%. Nonetheless, lenders typically prefer borrowers with a lower ratio.
Your debt-to-income ratio is just one factor lenders consider when assessing your financial details as you begin the loan pre-approval process.
Property Type
If you are purchasing a primary residence, either VA loans or conventional loans will work. Things become more complicated if you are considering buying a second home or an investment property.
VA Loans
A major contrast between VA loans and conventional loans is that VA loans are solely for primary residences. This means you can still consider duplexes or fourplexes, but for a VA loan, you need to plan on living in the property you buy.
Conventional Loans
You can purchase your primary residence, secondary home, or investment property using a traditional mortgage. Qualifications are stricter for secondary homes and investment properties.
For instance, you need to put down a minimum of 10% to buy a secondary home and at least 15% to purchase an investment property.
Program Fees
The program fees for VA loans helps to make up for the lack of down payment and mortgage insurance requirements. This helps to lower the cost of the loan for U.S. taxpayers.
VA Loans
A VA funding fee is a single upfront cost, typically ranging from 1.25% to 3.3% of the loan amount. The exact percentage varies based on whether you have used your VA loan benefit before and your down payment.
This fee aims to cover possible costs if the borrower fails to repay. Though it’s a one-time payment, it’s commonly included in the total loan amount, increasing your monthly payment and the overall interest paid over the loan term.
Veterans who receive VA disability compensation are exempt from paying this fee.
Conventional Loans
Conventional loans typically do not come with specific fees that are exclusive, such as the VA funding fee charged for VA loans. These fees are not present in conventional loan transactions.
Additional Factors to Consider
While understanding the comparisons mentioned above is important, there are more differences between these two types of loans that you should be aware of.
- Minimum Property Requirements (MPRs): VA loan properties must meet certain criteria to ensure the home is safe, sanitar, and structurally sound.
- Loan Limits: VA loans do not have loan limits, unlike conventional loans. Each county sets these limits, with many counties establishing a $726,200 limit for a single-family property in 2023.
- Mortgage Rates: Generally, when comparing rates for a typical 30-year VA loan and a 30-year conventional loan, VA loans typically feature lower interest rates. The difference in percentage usually falls between 0.25% to 0.42%.
- Closing Costs: The VA imposes a cap on closing costs and limit what borrowers can pay for through “non-allowable fees.” This can make VA loans more financially favorable if you’re on a tight budget.

Benefits of a VA Loan vs. Conventional Loan
While VA loans and conventional loans each have their own strengths, a VA loan offers specific advantages that are quite helpful for homebuyers.
- No Down Payment: If you qualify for full VA benefits, you don’t need to make a down payment. This speeds up your path to owning a home since you don’t have to save up a large down payment.
- Competitive Interest Rates: VA loan interest rates are usually lower than those for conventional loans, helping you save money over the loan’s duration.
- Limits on Closing Costs & Fees: VA loans have specified fees that buyers are not allowed to pay, known as “non-allowable fees,” and can include up to 4 percent in seller concessions.
- VA Funding Fee Exemptions: Some individuals may not have to pay the VA funding fee, which is typically 2.15 percent of the loan. Being exempt from this fee is a major advantage.
- No Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): Avoiding mortgage insurance for the entire loan term can save a homeowner thousands of dollars in the long term. This is an additional expense that VA homebuyers do not need to concern themselves with.

When VA Loans Make the Most Sense
If any of the following sound like you, then a VA loan makes the most sense.
- You’re struggling to save for a down payment
- You are buying a primary residence
- You would prefer to use your savings for something else, like an emergency fund
- You’d like to avoid PMI
- You’re a service member who has earned a Purple Heart, or a veteran with service-connected disabilities, making you eligible for a funding fee waiver

When Conventional Loans Make the Most Sense
If any of the following sound like you, then a conventional loan makes the most sense.
- You can afford to put down 20%
- You’d like to have immediate equity in your home
- Your credit score is excellent
- You want a lower monthly mortgage payment
- You’re buying a second home or investment property

Key Takeaways From VA Loans vs. Conventional Loans
VA loans offer cost-effective advantages and a smooth approval process.
Nonetheless, conventional loans may also provide beneficial terms depending on the lender.
When you have access to both VA loans and conventional loans, compare their requirements.
You might discover that one suits your circumstances better than the other.
For instance, if you’re a first-time homebuyer, a VA loans’ mortgage requirements might be more attainable.
On the other hand, if you’re a current homeowner aiming to buy a second home or an investment property, you’ll have to seek financing through a conventional loan.
If you’re ready to get started on your home-buying journey, Helen Painter Group Realtors is here to offer our expertise and local knowledge.
A long-standing and trusted Fort Worth real estate agency, we’ve been serving buyers and sellers since 1958.
With over six decades of success behind us, you’ll surely have peace of mind knowing your best interests are being represented each step toward buying or selling a home.
To learn more or speak with an agent, feel free to give us a call at (817) 923-7321 or contact us.

